Applications
Find your area of interest and read more about what has been done in your field of research.

Applications
Find your area of interest and read more about what has been done in your field of research.

Brain Tumors
Applying Random Walk Imaging’s software protocols in brain tumors has attracted significant interest. Brain tumor microstructure acquired with our protocols has been correlated to histopathology, which is the gold standard for diagnosis. Several ongoing studies on grading, follow-up of treatment and surgical planning have been presented at conferences.
- Tensor-valued diffusion MRI in under 3 minutes: An initial survey of microscopic anisotropy and tissue heterogeneity in four brain tumor types
- The link between diffusion MRI and tumor heterogeneity: Mapping cell eccentricity and density by diffusional variance decomposition (DIVIDE)
- Quantification of microscopic diffusion anisotropy disentangles effects of orientation dispersion from microstructure: Applications in healthy volunteers and in brain tumors.

Cardiac
Movement pose a great challenge for acquiring diffusion MRIs, and the beating of the heart has limited the use of these methods on this organ. However, using motion-compensated sequences when acquiring images, our software protocols for diffusion MRI has been successfully used for in-vivo imaging of the heart.

Clinical Implementation
Our software protocols for advanced diffusion MRI were initially developed for NMR microimaging systems. To transfer the methods from these systems, there has been numerous studies of the necessary adaptations for clinical scanners, including sequence optimization to reduce scan times, as well as ways to minimize artifacts.
- Multidimensional diffusion MRI with spectrally modulated gradients reveals unprecedented microstructural detail
- Maxwell-compensated design of asymmetric gradient waveforms for tensor-valued diffusion encoding
- Tensor-valued diffusion encoding for diffusional variance decomposition (DIVIDE): Technical feasibility in clinical MRI systems
- Liquid crystal phantom for validation of microscopic diffusion anisotropy measurements on clinical MRI systems
Kidney
It has been shown that novel information of the kidney microstructure, not accessible by conventional diffusion encoding, can be probed in-vivo by the use of our software protocols for advanced diffusion MRI.

Multiple Sclerosis
Compared to conventional diffusion encoding methods, applying our diffusion MRI software protocols significantly improves the ability to capture white matter changes in subjects with Multiple Sclerosis. The observed changes have been correlated to clinical scores, and highlight this tool as a potentially complementary MRI modality to track disease progression and treatment response.

Neuroscience
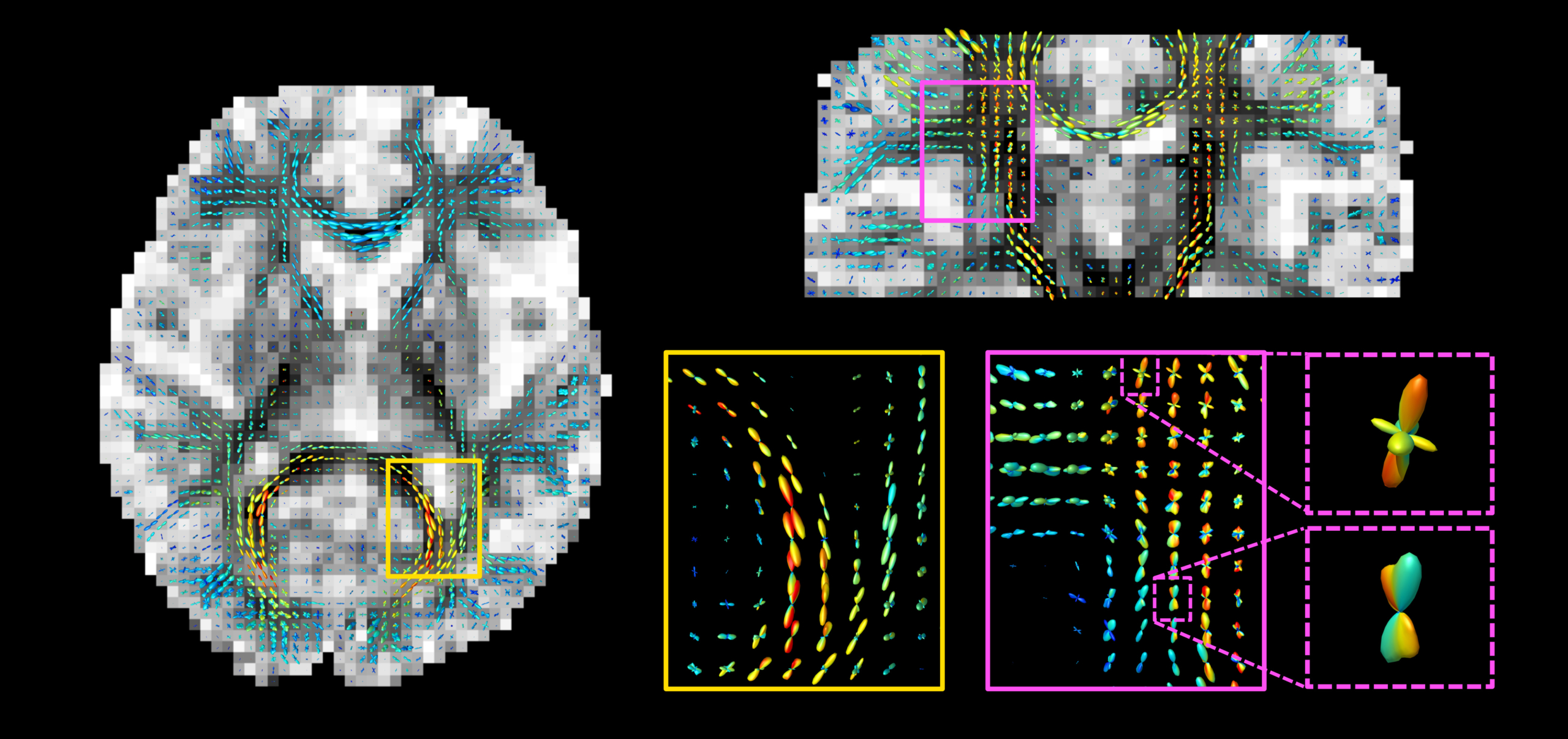
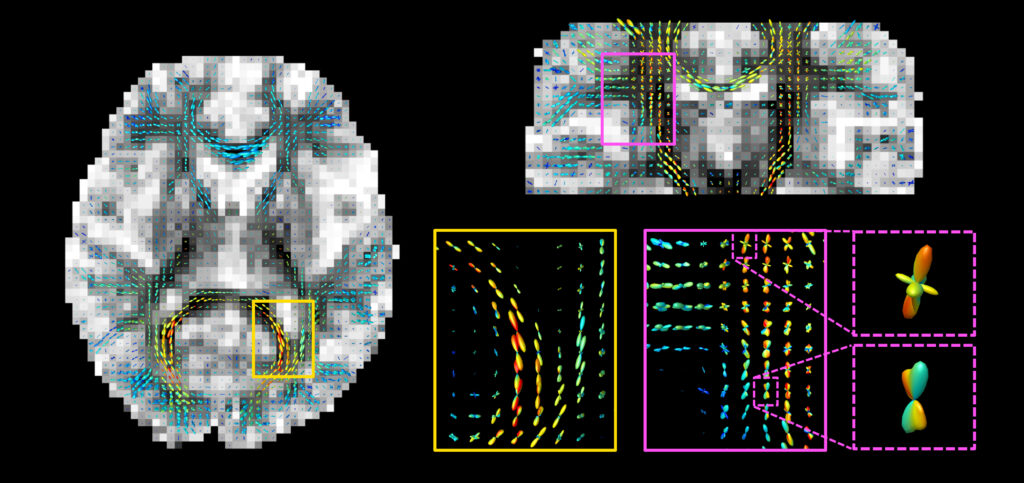
Our software protocols for advanced diffusion MRI methods have been used in the brain to study its microstructure in more detail and both changes in white and gray matter have been investigated. Applying tractography to our methods improves outcomes in areas where identification of tracts has previously been difficult, such as at fiber crossings.

Additional RWI Methods
There are several other aspects of our software protocols for advanced diffusion MRI. Two of these have already been used in research and are highlighted here.
With a specific subset of our software protocols, it is possible to quantify the rate of exchange between microscopic tissue environments – which after analysis can be converted to a quantitative measure of cell membrane permeability. Another software protocol can distinguish between the patterns water movements make in tissue versus that in capillaries, which allows for quantification of blood capillary density.
- Apparent exchange rate mapping with diffusion MRI
- Filter-exchange PGSE NMR determination of cell membrane permeability
- Optimal experimental design for filter exchange imaging: Apparent exchange rate measurements in the healthy brain and in intracranial tumors
- Quantification of microcirculatory parameters by joint analysis of flow‐compensated and non‐flow‐compensated intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) data

Epilepsy
Multidimensional diffusion MRI methods have been used to study epilepsy, revealing the underlying microstructural changes in malformations of cortical development. This underscores the potential of this tool to non-invasively explore previously unattainable underlying sources of epileptic seizures.

Breast Cancer
MDD can be applied to breast cancer patients providing both conventional ADC values, consistent with literature, and novel contrasts reporting on cell shapes and tissue composition.
This independent characterization of cell shapes and orientations in addition to cell density probed by conventional DW MRI has the potential to improve current diagnosis of breast cancer.

Prostate Cancer
MDD for prostate cancer, applied in a successful proof of concept study submitted to RSNA-2020 and XXX (Greta please check and add some text)


